TOKYO, Jun 8, 2022 – (ACN Newswire) – TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K. (Head office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; Representative Director & CEO: Koichiro Tanaka), which operates the TANAKA Precious Metals manufacturing business, announced today the launch of its RE Series of recycled precious metals, which uses 100% recycled materials as the source of gold, platinum, and other precious metals.
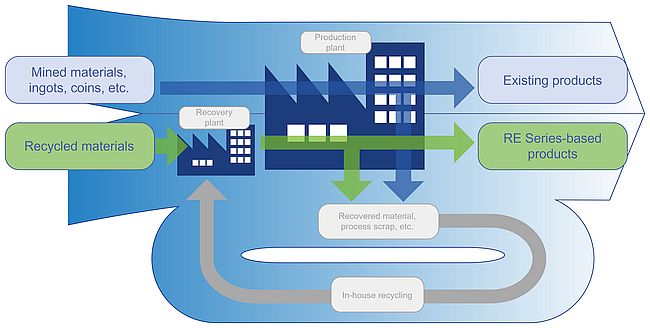 |
| RE Series industrial-use product flow |
 |
| RE Series logo |
The RE Series is composed of materials refined from recycled precious metals only rather than from sources such as mined bullion. TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo has been operating a recycled precious metals business since it was established. It has now expanded its RE Series production line to manufacture products that use 100% recycled precious metal materials. In the future, the company will begin manufacturing and supplying products that use RE Series materials. In April 2022, TANAKA began using RE Series gold to supply PGC-RE, a gold compound for plating, as its first product using RE Series materials.
Through its RE Series, TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo hopes to continue contributing to the creation of the Sound Material-Cycle Society and to the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, both of which are needed worldwide. To help address social issues through the expansion of RE Series materials, the total volume of recycled materials needs to be increased. To achieve this, the company is calling on its customers for support as it increases the volume of recycled materials that it can accept to incorporate even more precious metals into the resource-recycling loop. At the same time, it will continue to drive research and development in its precious metals recycling business.
Over recent years, there has been a strong global push for companies to respond to issues such as the creation of the Sound Material-Cycle Society, carbon neutrality, SDGs, and ESG management. Within the precious metals market, customer needs and the responsibility of a company working with industrial businesses are creating an urgent need to offer sustainable materials and products.
The business of mining gold, platinum, and other precious metals requires vast amounts of energy. Also, because precious metals themselves are rare natural resources with limited reserves, expansion of the RE Series will improve the efficiency of use by reducing requirements for newly mined materials. Reductions in CO2 will also lead to reduced environmental impacts, which helps to create a more sustainable society.
Precious metal recycling is a key business at TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo. To contribute to global trends, the company is expanding its production line for RE Series materials, which are 100% recycled precious metals.
TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo and Precious Metal Recycling
Ever since it was established in 1885, TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo has operated a precious metal recycling business as one of its core businesses, with a comprehensive system of management within the Group from product recovery to refining and remanufacturing into new products. This total solution, a one-stop service for recycling, processing, and manufacturing, is an end-to-end process from material procurement through to processing, manufacturing, sales, and recycling without using on-market trading. This enables reduced lead times for customers and reduced costs of material procurement.
An important element of precious metal recycling is the ability to analyze the quantities of precious metals present in recycled materials, including those from automotive catalysts, industrial production scrap, and plant output. With advanced precious metal analysis technologies*1 developed through many years of research and development of precious metals, TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo is able to accurately evaluate materials recovered from customers.
Status of Precious Metal Recycling in Japan and Globally
Gold, platinum, and other precious metals are natural resources with low production volumes and limited reserves. Due to the uneven distribution of resources globally and the environmental destruction that mining causes, the availability of precious metals is expected to become even tighter in the future. Accordingly, research and development of precious metal recycling have continued around the world and have become more sophisticated over recent years.
In Japan, with the 1998 enactment of such things as the Home Appliance Recycling Law, legislation is being put in place, and technologies are being developed in the area of metal recycling. While the recycling of precious metals like gold and platinum is comparatively advanced, the recycling rates of gold and platinum group metals are around 30%, so there is still a lot of room for improvement.
In the European Union, where recycling is an important part of their economic activities, they have decided that recycling activities have been insufficient to date. Within the EU, they adopted the Circular Economy Package in 2015 with the aim of changing into a circular economy that uses circulative resources. China has also been focusing on recycling policies recently as it rapidly changes its industrial model through legislation.*2
About TANAKA Precious Metals
Since its foundation in 1885, TANAKA Precious Metals has built a portfolio of products to support a diversified range of business uses focused on precious metals. TANAKA is a leader in Japan regarding the volumes of precious metals handled. Over the course of many years, TANAKA has not only manufactured and sold precious metal products for industry but also provided precious metals in such forms as jewelry and assets. As precious metals specialists, all Group companies in Japan and around the world collaborate and cooperate on manufacturing, sales, and technology development to offer a range of products and services. With 5,193 employees, the Group's consolidated net sales for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2021, was 1,425.6 billion yen.
Global industrial business website
https://tanaka-preciousmetals.com/
Product inquiries
TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K.
https://tanaka-preciousmetals.com/en/inquiries-on-industrial-products/
Press inquiries
TANAKA Holdings Co., Ltd.
https://tanaka-preciousmetals.com/en/inquiries-for-media/
*1 One measure of precious metal analysis capabilities is the status of Good Delivery Referee, an accreditation of the LBMA and LPPM, the most prestigious organizations in the field globally, which TANAKA Kikinzoku Group received as one of only five companies globally and the only company in Japan and the rest of Asia. The Group is also the first in Japan to acquire ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation for its analysis technologies for platinum, gold, silver, and palladium.
*2 Reference: TSC Foresight Vol.13, "Formulating Technical Strategies in the Area of Metal Recycling," December 2016, Technology Strategy Center (TSC), New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
Copyright 2022 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. http://www.acnnewswire.com